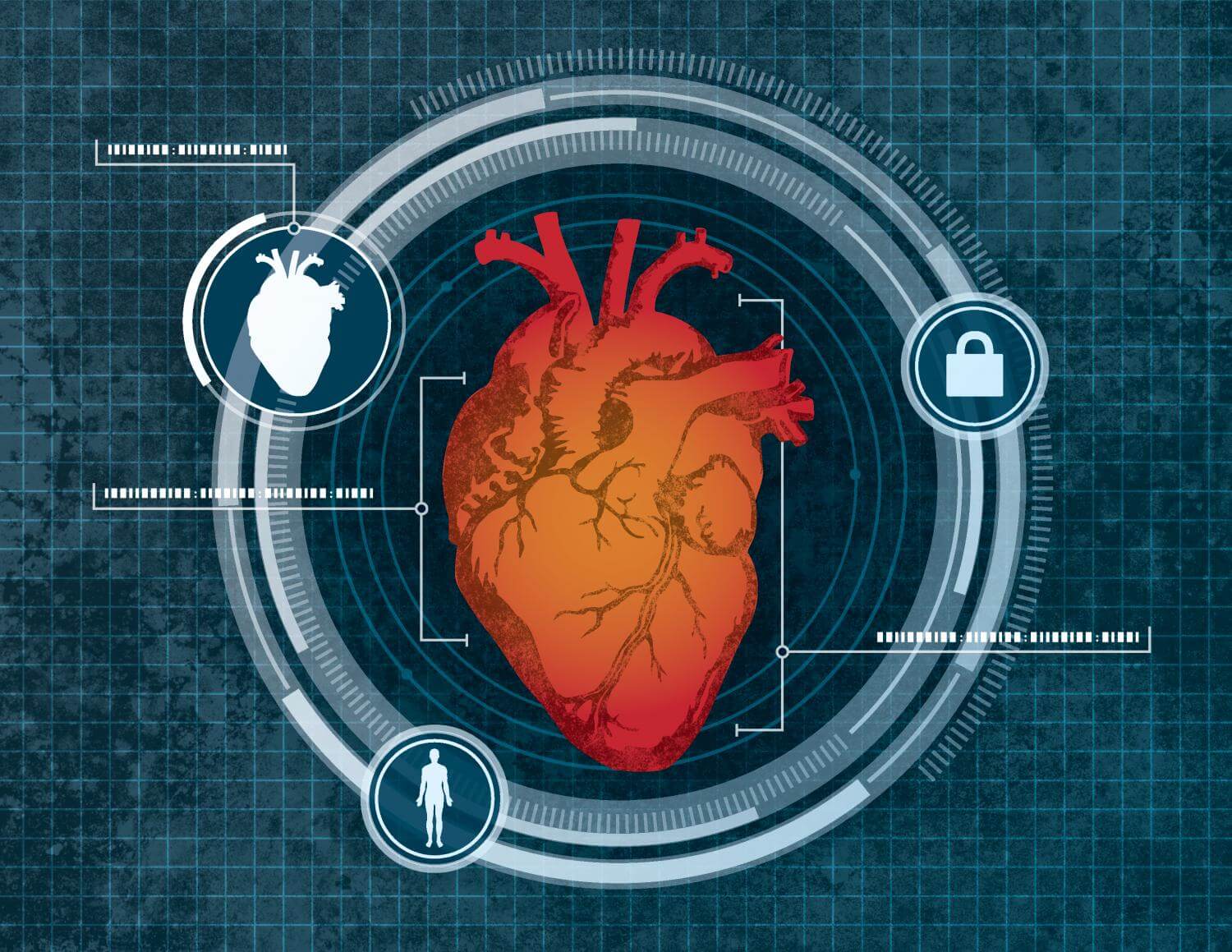
Fingerprint, iris, more recently facial scanning – these methods of authentication have been employed together or separately to keep user data safe. But they’re not foolproof – each has a weakness that hackers can’t wait to exploit. But researchers from the University at Buffalo are convinced they have found an even more ingenious way (this time, possibly unhackable) to secure our information – heart scanning #biomagic
Wenyao Xu, PhD, the lead author of the research ,came up with the security system that relies on a user’s heart to keep data safe. His technology takes in the geometry of the heart – shape, size, movement – to accurately identify the owner of a device. Xu sees his system implemented in computers, smartphones and at airports.
For the registration process, the system uses a Doppler radar with a lower signal strength than that of Wi-Fi. “The reader is about 5 milliwatts, even less than 1 percent of the radiation from our smartphones“, explains Xu. It doesn’t pose a threat to the health of the user.
The first scan takes about eight seconds. Then, the tech continuously monitors the heart, recognizing it automatically when it’s in the range. This implies that the user doesn’t need to authenticate every time they use the device or log off, for that matter.
The team’s discovery represents the first non-contact remote device that uses the hearts’ geometrical traits for identification. Xu is convinced that the solution is not only innovative, but more efficient than the ones already on the market: “No two people with identical hearts have ever been found“. Moreover, during a person’s lifetime, the heart doesn’t dramatically change shape, unless it suffers serious damage.
Researchers are looking into ways of miniaturizing the technology so it could be installed in computer keyboards, phones and other gadgets.
Follow TechTheLead on Google News to get the news first.