The most awaited feature of Google Pixel 4 was astrophotography mode. It not only played on the strengths Google phones have – camera software – , but it also promised to fill a gap in phone photography, as most flagship phones struggle with night sky photography. So how did Google try to fill that gap? Here are just five of their tricks.
Pixel 4 may have its drawbacks, but astrophotography is one of their few major perks. We talked about it briefly before the phone came out and now, we have an official rundown of how the Google team created this concept
Exposures of up to 4 minutes
Up until Pixel 4, Google phones had the capability of capturing 4 minute exposures but actually came up with 1 minute ones. This time, the engineers realized the best per frame exposure time for shooting the night sky was 16 seconds so they rounded up the time it would take to get 15 such frames and came to a four minute overall exposure.
Concealing bright spots
During these long exposure, bright spots that have no business being the shot are a given. To discern between the artificial ones and the real ones in the photo, the camera software in Pixel 4 “compares the value of neighboring pixels” in the frame and across all captured frames. Once they are identified, the foreign pixels can be concealed using the average value of the pixels in their proximity.
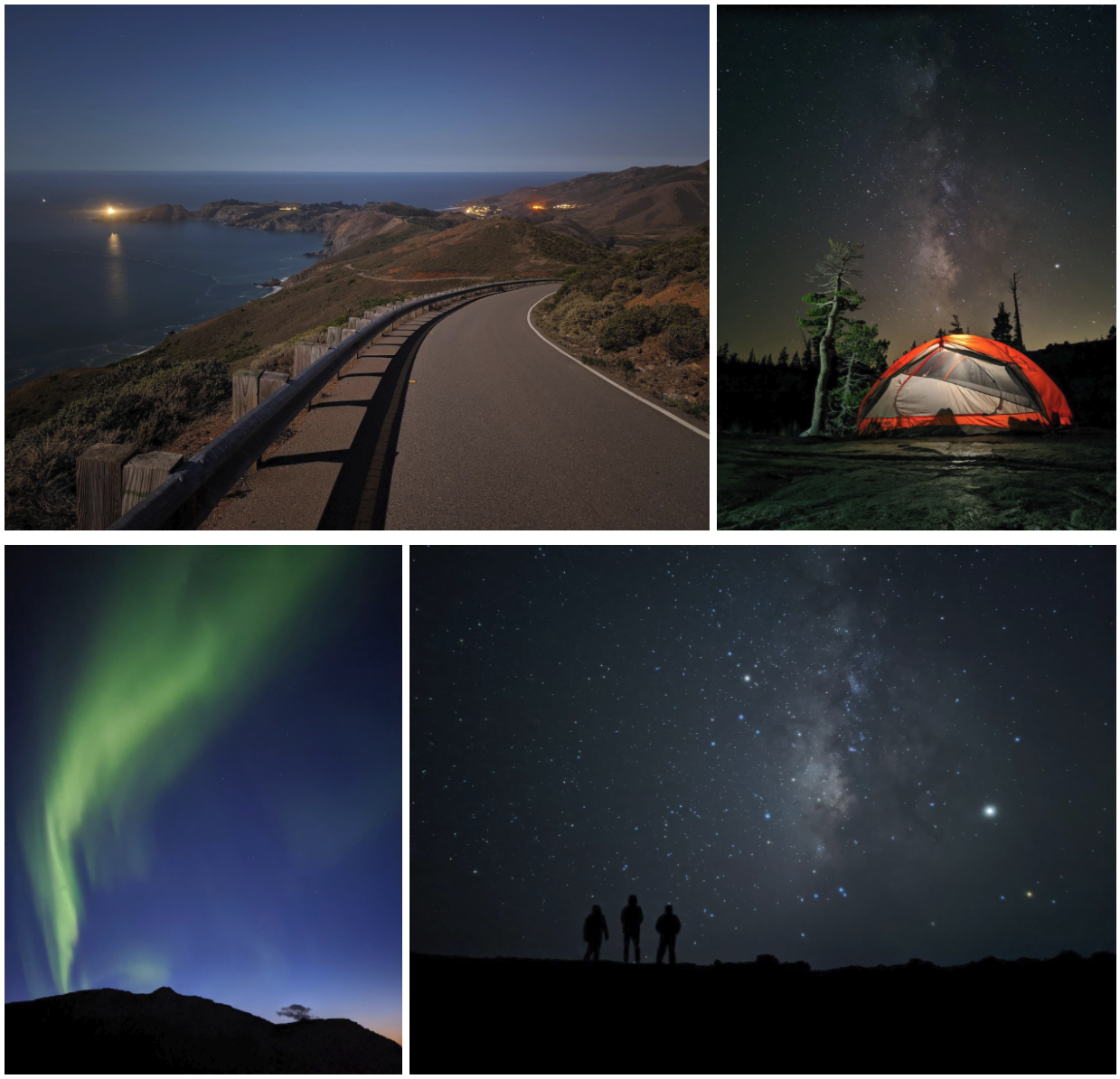

Using the last captured frame as direction for your composition
“At light levels below the rough equivalent of a full moon or so, the viewfinder becomes mostly gray — maybe showing a few bright stars, but none of the landscape — and composing a shot becomes difficult,” Google explains. So, they figured out that a reference could be the last captured frame.
To get the composition desired, the user just has to move the phone “while the exposure continues. Once the composition is correct, the initial shot can be stopped, and a second shot can be captured where all frames have the desired composition.”
The post-shutter autofocus technique
In extreme low-light, autofocus is a headache. To get it right, Google came up with a post-shutter autofocus technique. This implies getting two autofocus frames of up to a second each after a user hits the shutter key. These are just guidelines for the actual details you want to focus on and are not preserved for the final shot.
If this fails, then the focus goes to “infinity” or the user will have to focus manually.

AI to darken the sky
Different levels of light in the sky and around it can trick the camera to think that a daylight scene is occurring. To prevent that, the Pixel 4 phone uses a neural network trained on over 10,000 images to darken the sky. By detecting it in the first place, it can also make other useful adjustment such as reducing the noise and increasing the contrast.
The only thing they are still struggling with? Getting a correct shot of a full moon and the lit objects on the ground.
Follow TechTheLead on Google News to get the news first.