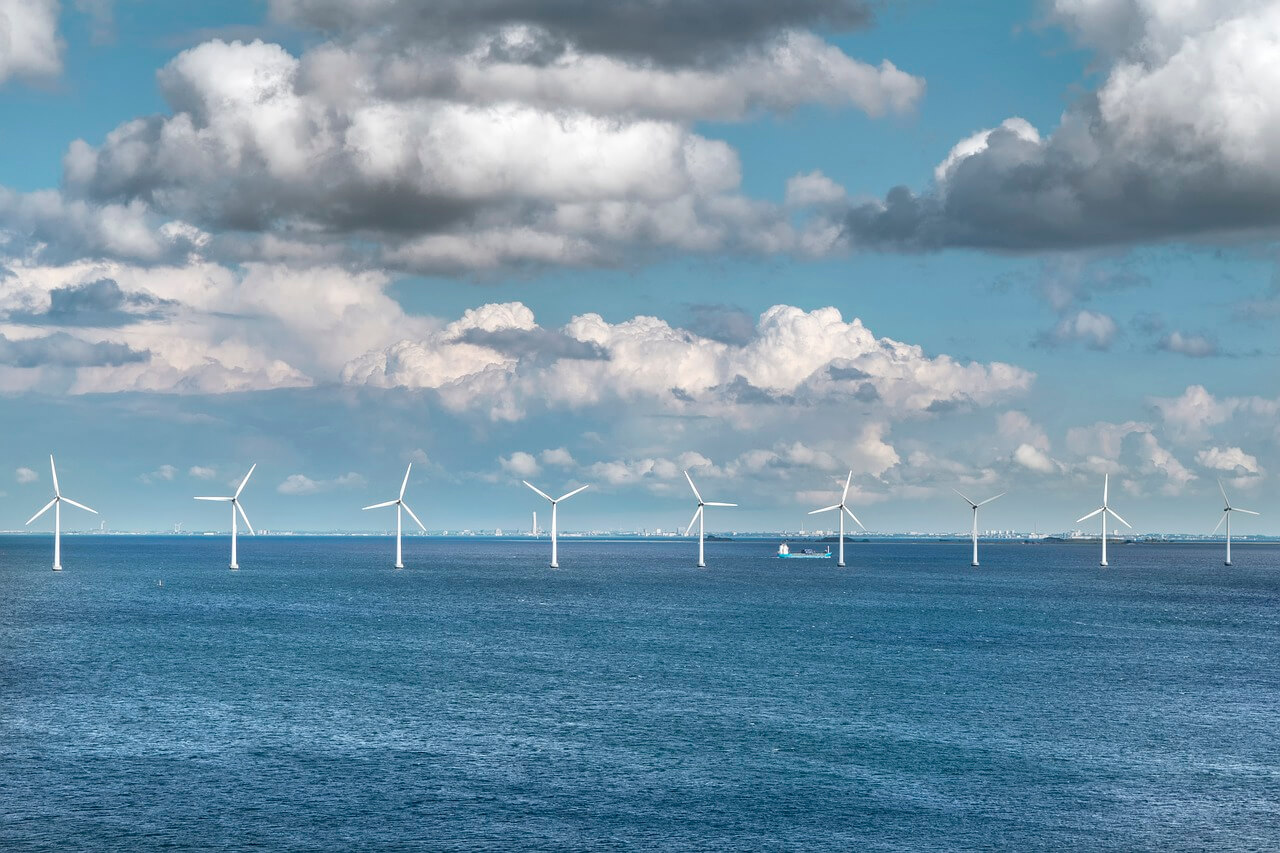
The shift toward renewable energy sources is gaining momentum, with offshore wind farms playing a pivotal role in this transition. These farms — with their massive turbines anchored in the sea — harness the power of ocean winds to generate clean, sustainable energy. This technological marvel is a testament to human innovation and people’s commitment to a greener planet.
However, as people integrate more technology into the energy infrastructure, the importance of cybersecurity becomes unmistakably clear. These offshore giants are digital fortresses that require robust protection.
Cybersecurity ensures these critical assets remain resilient against digital threats. It safeguards the energy they produce and the control systems that keep them running smoothly. In this era of increasing cyberthreats, securing offshore wind farms is imperative for the reliability and stability of future power supply.
The Growing Importance of Offshore Wind Energy
Offshore wind energy is experiencing a remarkable boom globally. It reflects an accelerating shift toward renewable power sources. This surge comes with the quest for sustainable, clean solutions to meet growing electricity demands while reducing carbon emissions.
In the U.S., wind power capacity has soared by 60% since 2017, reaching approximately 143 gigawatts (GW). This growth exemplifies wind’s significant role in the national energy mix, contributing to energy security and environmental goals.
The benefits of offshore wind energy for global sustainability are vast. It provides a renewable power source that reduces dependency on fossil fuels, lowers greenhouse gas emissions and mitigates climate change. Additionally, these farms can generate substantial amounts of electricity, enhance power production efficiency and reduce transmission losses.
Central to the operation of these offshore wind farms is the reliance on digital technology. Digital innovations are integral to maximizing efficiency and reliability, from remote monitoring and control systems to predictive maintenance and performance optimization. The digital backbone enables real-time data analysis, which is essential for informed decision-making and agile responses to changing wind conditions.
Cybersecurity Challenges for Offshore Wind Farms
Offshore wind farms face unique cybersecurity challenges because of their complex digital infrastructure and critical energy grid roles. They integrate advanced monitoring, control and data analysis technologies, making them vulnerable to cyberthreats.
One of the primary concerns is the multitude of remote access points and control systems. These are essential for efficient operation and allow multiple entities to remotely monitor, control and collect data from the wind farms. However, it also means there are more avenues through which cyberattackers can penetrate the system.
Potential vulnerabilities include weak points in the communication networks between the offshore turbines and onshore control centers. Moreover, there is inadequate encryption of data transmission and the possibility of unauthorized access through phishing attacks or the exploitation of software vulnerabilities.
The complex supply chain and involvement of multiple stakeholders in managing and operating wind farms further compound these risks, as each party may have different cybersecurity practices and standards.
A successful cyberattack could lead to power outages and affect thousands of homes and businesses. It could also result in data breaches, which can compromise sensitive operational data, personal information or national security information, given the critical infrastructure status of the energy supply.
Further, the financial impact of such incidents could be substantial, involving repair costs, regulatory fines and reputational damage. The necessity for stringent cybersecurity measures is apparent — to protect the infrastructure and ensure the reliability and security of the energy supply chain.
Current Measures in Place
An array of standards and regulations fortifies the cybersecurity landscape for offshore wind farms to safeguard these vital energy infrastructure components. Industry adherence to guidelines from third-party organizations underscores a commitment to implementing best practices for protection and operational technologies. These frameworks establish a secure environment that can withstand the many cyberthreats facing the sector today.
Integrating information technology (IT) and operational technology (OT) significantly enhances offshore wind farms’ cybersecurity posture. This integration facilitates a seamless flow of data and control commands between IT and OT systems.
IT systems are responsible for data analytics and business management. Meanwhile, OT systems control physical processes and equipment. Such a harmonious integration boosts operational efficiency, reduces errors, and strengthens detection and response mechanisms against cybersecurity threats. Enhanced communication between these systems enables real-time monitoring and swift action to mitigate potential risks.
Technological innovations are continuously reshaping the cybersecurity defenses of offshore wind farms, introducing more robust protections against cyber intrusions. Applying advanced encryption techniques, deploying blockchain for secure data transactions and utilizing machine learning to detect anomalies exemplify these forward-thinking approaches.
Moreover, the move toward zero-trust architectures offers a proactive defense strategy, assuming no internal or external entity is trustworthy without verification. These developments and ongoing training for cybersecurity personnel ensure offshore farms can power homes securely against the evolving digital threats of the modern world.
Strengthening Offshore Wind Security
Embracing smart grid technology is pivotal to enhancing offshore wind energy’s cybersecurity framework. Smart grids with advanced communication and control capabilities can improve security measures. With over 9,200 electric generating units and more than 300,000 miles of transmission lines, these grids facilitate real-time data collection and analysis to enable proactive threat detection and response.
Integrating these technologies into offshore wind energy infrastructure enhances efficiency and reliability. It fortifies defense against cyberthreats, allowing automated updates, threat intelligence sharing and advanced anomaly detection.
Moreover, collaboration between governments and the private sector is essential. Such partnerships can drive the development of robust cybersecurity standards and practices tailored to the unique needs of the offshore wind sector. Together, these entities can foster an environment of knowledge sharing and mutual support, which is crucial for staying ahead of cyberattackers.
For instance, the U.S. Department of Energy’s initiative to launch a $30 million grant program to develop cybersecurity tools for clean energy infrastructure underscores the importance of governmental support in bolstering the sector’s cyber defenses. This program is a step toward protecting the nation’s clean power assets. It encourages innovation in cybersecurity solutions tailored to renewables.
By investing in these areas, stakeholders can ensure offshore wind energy’s resilience and security. This approach safeguards it against the evolving landscape of cyberthreats and contributes to a secure, sustainable future.
Securing the Future of Offshore Wind Energy
Robust cybersecurity measures ensure the reliability and integrity of offshore wind energy and protect it from evolving cyberthreats that could compromise power and national security. As this sector continues to expand, prioritizing cybersecurity will safeguard clean energy infrastructure and reinforce public trust in renewables as a secure and sustainable source for the future.
Article contributed by Emily Newton.
About the author: Emily Newton is the Editor-In-Chief of Revolutionized, a magazine exploring innovations in science and industry that shares ideas to promote a better tomorrow. She enjoys writing and researching about how technology is changing the world.
Follow TechTheLead on Google News to get the news first.